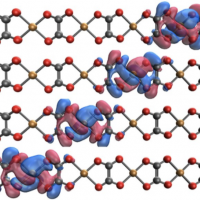
Excited-State Methods in Q-Chem
Overview of Excited-State Capabilities
Q-Chem offers many excited-state methods, from CIS and TDDFT and their spin-flip variants to the high-level equation-of-motion coupled-cluster (EOM-CC) and the algebraic diagrammatic construction (ADC) methods. The table below summarizes excited-state methods available in Q-Chem.
| Method | Analytic Gradient | Analytic Hessian |
|---|---|---|
| Configuration interaction singles | ||
| CIS | ✓ | ✓ |
| RPA | ✓ | ✓ |
| Extended (X)CIS | ✘ | ✘ |
| SF-XCIS | ✘ | ✘ |
| Spin-Adapted XCIS | ✘ | ✘ |
| CIS with perturbative doubles | ||
| CIS(D) | ✘ | ✘ |
| RI-CIS(D) | ✓ | ✘ |
| SOS-CIS(D) | ✓ | ✘ |
| SOS-CIS(D0) | ✓ | ✘ |
| Time-dependent DFT | ||
| TDDFT | ✓* | ✓* |
| Spin-Flip (SF) TDDFT | ✓ | ✘ |
| TDDFT with a Reduced Single-Excitation Space | ✓ | ✓ |
| ∆SCF | ||
| MOM | ✓ | ✓ |
| ROKS with SGM | ✓ | ✘ |
| Non-orthogonal CI (NOCI) | ||
| NOCI | ✘ | ✘ |
| NOCIS/1C-NOCIS | ✘ | ✘ |
| Static Exchange (STEX) | ✘ | ✘ |
| Equation-of-motion coupled cluster theory (EOM-CC) | ||
| EOM-EE(SF)-CCSD** | ✓*** | ✘ |
| EOM-IP(EA)-CCSD** | ✓*** | ✘ |
| EOM-DIP(DEA)-CCSD** | ✘ | ✘ |
| EOM-CC/C-PCM | ✘ | ✘ |
| EOM-CCSD with Core-Valence Separation (CVS) | ✘ | ✘ |
| Algebraic diagrammatic construction (ADC) | ||
| RI-ADC | ✘ | ✘ |
| Spin Opposite Scaling ADC(2) | ✘ | ✘ |
| ADC with CVS | ✘ | ✘ |
| SF-ADC, IP-ADC, EA-ADC | ✘ | ✘ |
| ADC/SS-PCM | ✘ | ✘ |
| FDET-ADC | ✘ | ✘ |
| Restricted active space (RAS) | ||
| RAS-CI | ✘ | ✘ |
| RAS Spin-Flip (SF) | ✘ | ✘ |
* Not for all exchange-correlation functionals.
** RI and CD variants are also available.
*** RHF and UHF reference only, including RI and CD implementations.
Properties and Analysis
-
Analytic gradients are available for many methods
-
Analytic Hessians enable fast frequency calculations for TDDFT
-
Wide variety of properties including non-linear optical response and electronic couplings
Want to try Q-Chem?