Treating Environmental Effects: Implicit and Explicit Solvent Models
-
Popular implicit solvation models:
-
SM8, SM12, SMD, COSMO, C-PCM, SS(V)PE, IEF-PCM, CMIRS, and more;
-
Intrinsically smooth discretization of the solute/continuum interface;
-
Poisson equation solver for anisotropic dielectric boundary conditions.
-
-
Effective fragment potential (EFP) for modeling explicit solvent with polarizable embedding:
-
Available for ground and excited states;
-
Interfaced with DFT and wave function based methods;
-
Extension to biomolecules is available;
-
Built-in library of effective fragments.
-
-
Density embedding is available for selected methods.
-
Many-body expansion can incorporate solvent molecules at a QM level.
-
Stand-alone electrostatic embedding (QM/MM) capabilities:
-
Available for ground or excited states;
-
Integration with PCM models (QC/MM/PCM);
-
Many-body expansion can incorporate solvent molecules at a QM level.
-
-
Interface to CHARMM:
-
QM/MM using CHARMM’s extensive set of sampling methods;
-
Full QM/MM Hessian or "mobile block-Hessian" approximation facilitate study of vibrational entropic effects or large-scale conformational changes.
-
-
Interfaces with GROMACS and NAMD are available.
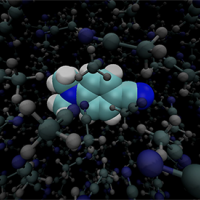
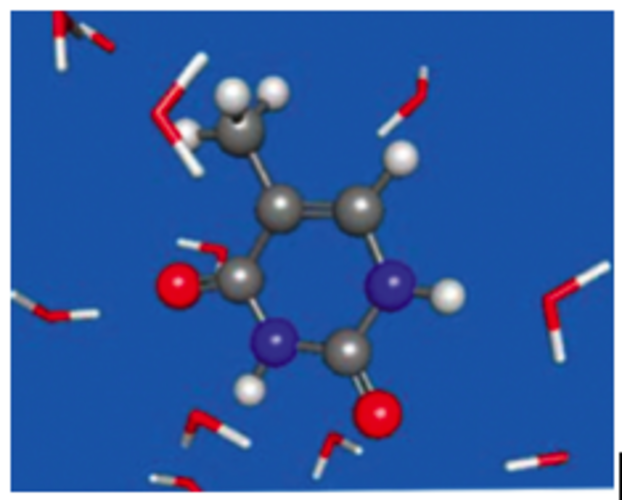 EFP used to compute ionization energies and redox potentials of bulk-solvated species
EFP used to compute ionization energies and redox potentials of bulk-solvated species
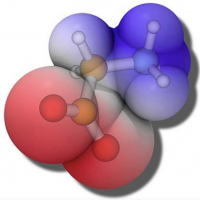
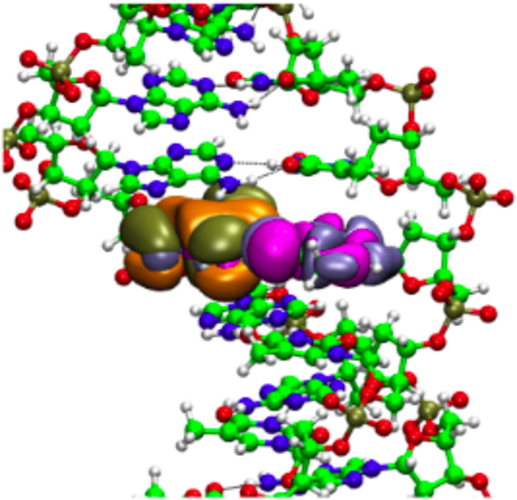 HOMO and LUMO of a Watson-Crick base pair in a QM/MM description of double-stranded DNA
HOMO and LUMO of a Watson-Crick base pair in a QM/MM description of double-stranded DNA
Want to try Q-Chem?